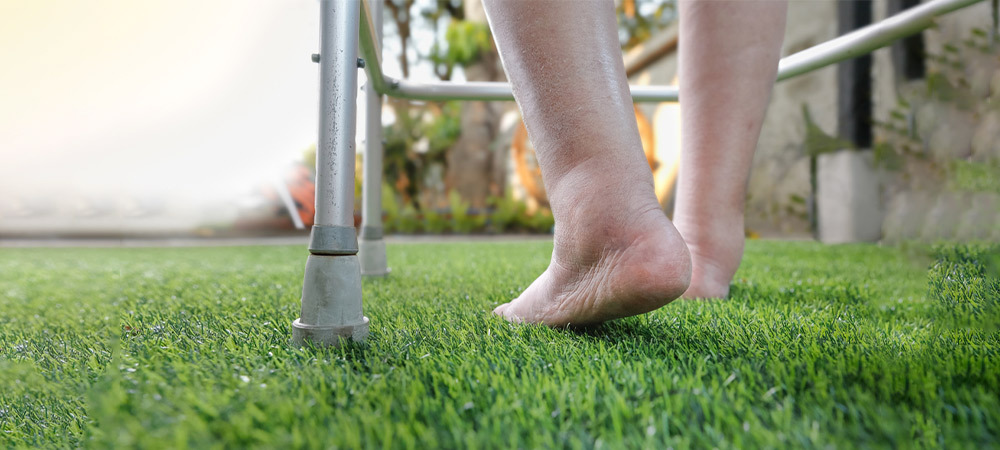
Venous hypertension is characterized by swelling, aching, and skin changes in the legs due to poor blood flow. It is caused by valve failure in the veins, often from prolonged standing, obesity, or deep vein thrombosis. Treatment may include compression therapy, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
What is Venous Hypertension?
Venous hypertension is a condition that affects the blood circulation in the veins, particularly in the lower limbs, where the veins struggle to pump blood back to the heart. This causes increased pressure in the venous system, leading to a range of symptoms and complications. If left untreated, it can lead to chronic discomfort, skin changes, and even ulcers. In this blog, we will explore what venous hypertension is, its symptoms, underlying causes, how it is diagnosed, and the available treatment options.
To begin with, venous hypertension refers to elevated blood pressure in the veins, primarily due to malfunctioning valves. Meanwhile, in healthy veins, one-way valves help direct blood flow toward the heart. However, when these valves become weak or damaged, blood can flow backward (a condition known as venous reflux) and pool in the legs
Symptoms of Venous Hypertension
Symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the condition. In the early stages, many individuals might not notice significant discomfort, but as the condition progresses, the symptoms become more apparent and uncomfortable.
1. Leg Swelling:
One of the first and most common symptoms is swelling in the lower legs and ankles, especially after long periods of standing or sitting. Moreover, this happens as blood pools in the veins, causing fluid to leak into the surrounding tissues.
2. Aching or Heaviness:
Many people with this condition report feelings of heaviness, aching, or tiredness in the legs. Additionally, it often worsens as the day goes on or after extended standing.
3. Varicose Veins:
The increased pressure in the veins can cause them to enlarge and become twisted, leading to varicose veins. Thus, these are often visible on the surface of the skin as blue or purple bulging veins.
4. Skin Changes:
Over time, it can lead to skin changes such as discoloration, thickening, and dryness. The skin around the ankles may take on a brownish or reddish color due to increased pressure and inflammation. Thus, this condition is called venous stasis dermatitis.
5. Leg Ulcers:
In severe cases, this can result in the development of painful ulcers, usually around the ankles. These ulcers can be slow to heal and may become infected if not properly treated.
Overall, it is important to recognize these symptoms early to prevent the condition from worsening. When symptoms are left untreated, they can lead to complications that may significantly impact one’s quality of life.
Causes of Venous Hypertension
This condition has multiple underlying causes, and it often results from a combination of factors that impair normal blood flow in the veins.
1. Valve Dysfunction:
One of the primary causes includes the failure of the one-way valves within the veins. Since, these valves are responsible for preventing the backflow of blood. When they become damaged or weakened, blood can pool in the veins, leading to increased pressure.
2. Prolonged Standing or Sitting:
Occupations that require long periods of standing or sitting, such as teaching or office work, can contribute to its development. Prolonged immobility reduces the effectiveness of the muscle pump mechanism in the legs, which is essential for moving blood back toward the heart.
3. Obesity:
Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins, making it harder for blood to return to the heart. This increased pressure can lead to valve dysfunction and venous reflux.
4. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT):
A history of DVT, where blood clots form in the deep veins of the legs, can damage the veins and valves, increasing the risk of venous hypertension.
5. Aging:
As we age, the veins naturally lose elasticity, and the valves become less efficient. Moreover, this is why this form of hypertension is more common in older adults.
Diagnosis of Venous Hypertension
Diagnosing this involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Physicians will assess for visible signs of venous disease, such as varicose veins, skin changes, and swelling. However, since not all symptoms are externally visible, further diagnostic tests are often required.
1. Doppler Ultrasound:
A Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test used to evaluate blood flow in the veins. It helps detect venous reflux and measure the degree of the condition by assessing how well the blood moves through the veins.
2. Venogram:
In some cases, a venogram may be ordered. This test involves injecting contrast dye into the veins and taking X-rays to look for blockages, clots, or other abnormalities.
3. Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI):
Although primarily used to assess arterial circulation, the ABI test can also be helpful in differentiating between venous and arterial causes of leg symptoms. Early diagnosis is critical in preventing further progression and avoiding more serious complications.
Venous Hypertension Treatment
When it comes to treatment options, the goals are to reduce symptoms, improve blood flow, and prevent complications such as ulcers or infections. Treatment options can range from lifestyle modifications to medical interventions, depending on the severity of the condition.
1. Compression Therapy:
Firstly, one of the most common treatments is the use of compression stockings. With their unique design, these stockings gently press against the legs to enhance blood flow and lessen edema. Overall, compression therapy is highly effective in managing symptoms and preventing the progression of venous disease.
2. Lifestyle Changes:
Making changes to daily habits can significantly improve venous health. Elevating the legs when resting, staying physically active, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting can all help reduce venous pressure. Regular exercise, particularly walking or other activities that engage the leg muscles, can boost circulation and support vein health.
3. Medications:
In some cases, medications such as diuretics may be prescribed to reduce swelling, or anticoagulants may be used if there is a risk of blood clots.
4. Sclerotherapy:
For patients with varicose veins or smaller spider veins, sclerotherapy may be recommended. This involves injecting a solution into the affected veins, causing them to collapse and eventually be absorbed by the body. As a result, over time, blood flow is redirected to healthier veins.
5. Endovenous Ablation:
This minimally invasive procedure uses heat from laser or radiofrequency energy to close off damaged veins. Blood is then rerouted through healthier veins, alleviating symptoms and reducing pressure in the affected area.
6. Surgical Options:
In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary. Procedures such as vein stripping or ligation can remove or close off damaged veins, while bypass surgery may be needed if there is a significant blockage in the larger veins.
7. Treatment of Leg Ulcers:
Lastly, if the condition has led to the development of leg ulcers, specialized wound care may be required. This could involve dressings, topical medications, and compression therapy to promote healing and prevent infection.
Conclusion
Venous hypertension is a common condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life if not properly managed. Therefore, recognizing the symptoms early and understanding the underlying causes are key to receiving appropriate treatment. Whether through lifestyle changes, compression therapy, or more advanced medical interventions, there are numerous options available to effectively manage and prevent its progression. If you suspect you may have this condition, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment tailored to your specific needs.