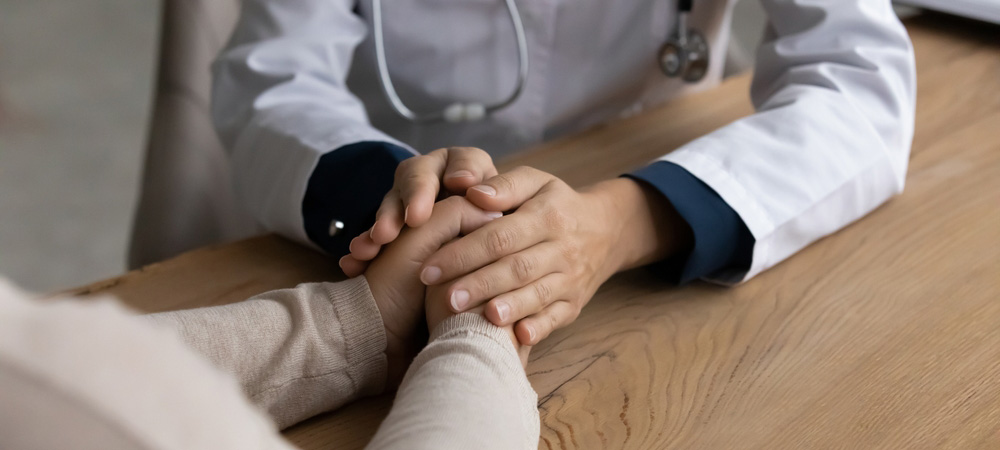
Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is a set of ethical and scientific quality standards for designing, conducting, recording, and reporting clinical trials involving human subjects. These guidelines are essential for safeguarding the rights, safety, and well-being of trial participants while ensuring the data collected is credible and reliable. This blog explores the importance of GCP principles in clinical trials, its significance for patients and healthcare professionals, and its fundamental principles.
What is GCP?
GCP, or Good Clinical Practice, sets an internationally recognized ethical and scientific quality standard for conducting clinical trials. It protects the rights and safety of trial participants while ensuring the credibility and reliability of the data collected. GCP principles guide researchers in every aspect of clinical trial design, conduct, and reporting. By adhering to these standards, clinical trials can achieve their intended purpose without compromising ethical values.
History of Good Clinical Practice
Early Clinical Research
Controlled clinical trials date back to 1747 when James Lind conducted the first comparative clinical trial on Spanish naval ships. Lind, troubled by the high mortality rate of scurvy among sailors, divided twelve men groups into two. Hence, the groups receiving citrus fruits, like lemons and oranges, showed significant improvements. Additionally, Lind’s findings later influenced naval fleets to include citrus in sailors’ diets, significantly reducing scurvy.
Evolution of Clinical Trials
The early 19th century saw the introduction of the placebo. By the mid-1940s, researchers were using double-blind controlled trials and randomized trials. While these methods led to significant medical discoveries, they also raised concerns about the safety, ethics, and protection of human participants. Furthermore, without standard regulations, there was no guarantee of participants’ safety or credible results.
Emergence of Ethical Guidelines
During World War II, unethical human experiments highlighted the need for ethical regulations beyond the Hippocratic Oath. The Declaration of Helsinki, issued by the World Medical Organization in 1964, provided guidance for medical research involving human subjects, building on the Nuremberg Code.
Standardization and the Birth of GCP
Despite these frameworks, regulatory inconsistencies persisted across regions and countries. To address this, the International Conference of Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) developed a universal set of guidelines in 1996, known as Good Clinical Practice (ICH-GCP). Additionally, these guidelines ensure that clinical trials are conducted ethically and that the data collected is credible and accurate. Furthermore, the participants’ rights and confidentiality are protected.
Importance of Good Clinical Practices
For Patients
For patients, GCP prioritizes their rights, safety, and well-being throughout the clinical trial process. GCP assures patients that researchers conduct the trial ethically and scientifically, fostering trust and willingness to participate. Informed consent is a crucial aspect of GCP, ensuring that patients are fully aware of the trial’s nature, potential risks, and benefits before participating. Furthermore, this transparency empowers patients to make informed decisions about their involvement in clinical research.
For Healthcare Professionals
For healthcare professionals, GCP provides a framework that guides the ethical and scientific conduct of clinical trials. It ensures that trials are conducted consistently and with integrity, leading to reliable data that can inform medical practice and decision-making. Compliance with GCP principles also helps healthcare professionals avoid legal and ethical issues that could arise from improperly conducted trials. GCP supports the advancement of medical knowledge and the development of new treatments and therapies.
The 3 Main Principles
GCP principles center around three main concepts: ethical principles, safety as a priority, and informed consent. These principles ensure that researchers conduct clinical trials in a way that respects participants’ dignity and rights while providing high-quality, reliable data.
Ethical Principles
Ethical principles form the cornerstone of GCP. Researchers should always conduct clinical trials according to GCP and applicable regulatory requirements. This means that trials must adhere to ethical standards that respect the dignity, rights, and welfare of participants. Ethical principles also ensure that the trials are scientifically sound and designed to provide meaningful data that can benefit medical science and patient care.
Safety as a Priority
Ensuring the safety and well-being of trial participants is a primary concern in GCP. Clinical trial activities should be designed to minimize risks and protect participants’ rights and health. /this involves careful monitoring of participants throughout the trial, prompt reporting of adverse events, and taking appropriate measures to address any issues that arise. By prioritizing safety, GCP helps to build trust in the clinical trial process and encourages participation.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is a fundamental principle of GCP. It ensures that clinical trial participants are well-informed about the nature of the trial, its potential risks and benefits, and their rights as participants. This process involves providing clear and comprehensive information to participants and obtaining their voluntary agreement to participate. Informed consent empowers participants to make educated decisions about their involvement in clinical research, promoting transparency and ethical conduct.
Are GCP Principles Only for Clinical Researchers?
While GCP principles primarily guide clinical researchers, they are not limited to this group alone. These standards also apply to healthcare providers, sponsors, regulatory authorities, and ethics committees involved in clinical trials. Furthermore, everyone engaged in the clinical trial process plays a role in ensuring adherence to GCP principles.
Healthcare providers must follow GCP guidelines when interacting with trial participants, ensuring informed consent and monitoring patient safety. Sponsors and regulatory authorities must ensure that trials comply with GCP standards, fostering ethical and scientifically sound research. GCP principles are a collective responsibility to safeguard participants and ensure high-quality research.
Why Ethical Principles Matter
Ethical principles are essential in clinical trials because they ensure that the research is conducted with respect for human dignity and rights. Adherence to ethical principles helps to prevent exploitation and harm to participants. It also ensures that the research is conducted with scientific integrity, providing valuable data that can improve medical knowledge and patient care. By following ethical principles, researchers can maintain public trust and support for clinical research.
The Role of Informed Consent
Informed consent is a vital component of GCP. It ensures that participants are fully aware of the trial’s purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits before agreeing to participate. This process promotes transparency and respect for participants’ autonomy. Informed consent also helps to protect participants from potential harm and exploitation. By ensuring that participants are well-informed, GCP promotes ethical conduct and trust in the clinical trial process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Good Clinical Practice is crucial in clinical trials to protect participants’ rights, ensure their safety, and provide reliable data. By adhering to GCP principles, we can advance medical knowledge and improve patient care while maintaining ethical standards. Understanding and applying GCP principles is essential for the success and credibility of clinical trials.