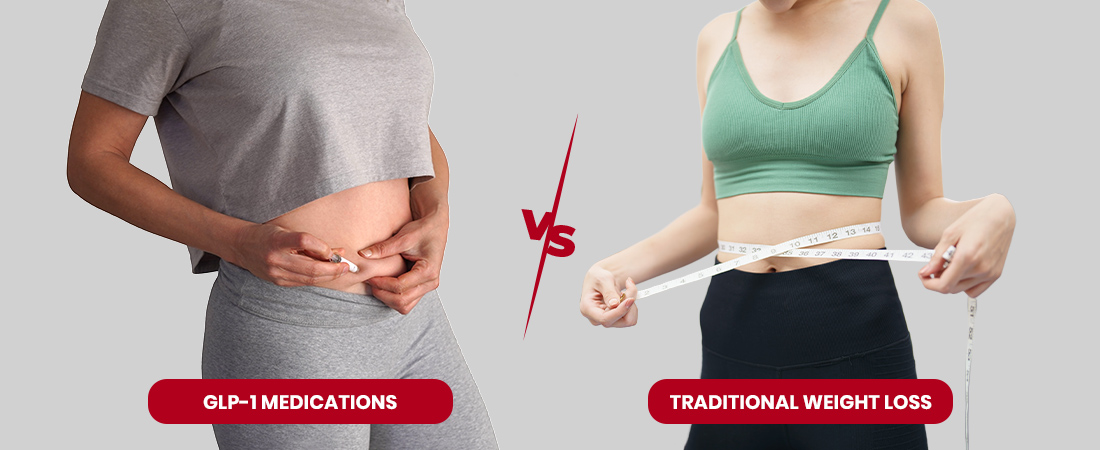
When it comes to weight management, many are now comparing GLP-1 medications vs. traditional weight loss approaches to understand which is more effective. Traditional methods focus on calorie control, exercise, and behaviour change, while GLP-1 medications work on a hormonal level to regulate appetite and metabolism. This shift in strategy is changing how we view sustainable weight loss.
GLP-1 Medications
GLP-1 medications, short for glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, are a class of drugs that mimic the action of a natural hormone called GLP-1. This hormone is produced in the gut and plays a key role in regulating blood sugar levels and controlling appetite.
By activating GLP-1 receptors in the body, these medications help individuals in several important ways:
- Curbing appetite: They signal the brain to promote a feeling of fullness, which helps reduce food intake and minimize cravings.
- Slowing gastric emptying: GLP-1 drugs delay the emptying of food from the stomach, making you feel fuller for longer after meals.
- Improving insulin response: These medications enhance insulin production when blood sugar levels rise and reduce the liver’s glucose output—making them especially beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes.
Popular GLP-1 Weight Loss Medications:
Several GLP-1 medications have shown promising results in promoting weight loss and managing blood sugar. Common examples include:
- Semaglutide
- Liraglutide
- Tirzepatide
Who Can Benefit from GLP-1 Medications?
GLP-1 therapy is most effective for individuals who:
- Have a BMI of 30 or higher, or a BMI of 27 or higher with obesity-related conditions.
- Struggle with persistent hunger or portion control despite diet and exercise efforts.
- Are managing metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
In clinical trials, some GLP-1 medications have helped patients lose 15–20% of their body weight, making them a significant advancement in weight management.
Also Read: Who is a Good Candidate for the GLP-1 Weight Loss Trial? What You Need to Know
Traditional Weight Loss Methods
In the ongoing comparison of GLP-1 medications vs. traditional weight loss, it’s essential to understand how conventional approaches have shaped weight loss efforts for decades. Traditional weight management relies heavily on lifestyle modifications, behavioral changes, and commercial programs.
1. Dietary Changes:
The cornerstone of most traditional weight loss strategies is calorie restriction—eating fewer calories than the body expends. Popular approaches include:
- Low-carb or low-fat diets
- Intermittent fasting
- Structured meal plans
While these methods can lead to short-term success, the body’s natural response to weight loss—slower metabolism and increased hunger—often leads to regained weight over time. Studies show that 80–95% of individuals eventually gain back the weight they lose.
2. Exercise Routines:
Exercise is widely promoted for its health benefits and modest support in weight loss. Common forms include:
- Cardiovascular exercises (walking, running, swimming)
- Strength training (to build muscle and support metabolism)
- Daily movement and activity tracking
However, on its own, exercise generally results in only 2–3% body weight reduction unless paired with strict dietary control.
3. Behavioral Therapy:
Changing one’s mindset and habits is key to sustaining weight loss. Techniques may include:
- Habit tracking and journaling
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to address emotional eating and thought patterns
These methods aim to build consistency but require high levels of motivation and time commitment.
4. Commercial Programs and Supplements:
Programs like Weight Watchers, Noom, and other app-based services combine diet plans, behavioral support, and community guidance. While helpful for some, results vary widely, and long-term success depends on adherence and individual factors.
Before the rise of GLP-1 medications, earlier prescription weight loss drugs offered limited effectiveness and often carried serious side effects. This makes the conversation around GLP-1 medications vs. traditional weight loss especially relevant, as newer treatments show more substantial and sustainable results with fewer risks.
Key Differences Between GLP-1 Medications and Traditional Methods
When comparing GLP-1 medications vs. traditional weight loss, it’s important to examine how they work, how effective they are, and what each approach requires for long-term success. Here’s how the two approaches differ in key areas:
1. Mechanism of Action:
- GLP-1 Medications regulate weight through hormonal and metabolic pathways. They mimic the natural hormone glucagon-like peptide-1, which controls appetite, slows gastric emptying, and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Traditional weight loss methods, on the other hand, rely heavily on a simple equation of calories in versus calories out—focusing on reducing food intake and increasing physical activity.
2. Speed and Amount of Weight Loss:
- GLP-1 medications typically lead to faster and more substantial weight loss. Clinical studies have shown reductions of up to 15-20% of body weight in some individuals.
- Traditional methods like diet and exercise generally produce slower and more variable outcomes, often requiring months or even years for modest results.
3. Sustainability and Long-Term Effects:
- With GLP-1 medications, many users need to continue long-term use to maintain weight loss. Once the medication is stopped, weight regain is common unless lifestyle changes are made.
- Traditional weight loss approaches are designed for lifelong behavioral changes, aiming to help individuals maintain results through consistent habits rather than medication reliance.
4. Cost and Accessibility:
- GLP-1 medications are often expensive and not always covered by insurance, which can be a major barrier for many individuals.
- Traditional weight loss methods vary widely in cost. While some commercial programs can be pricey, many options—like home workouts or basic dietary changes—are budget-friendly and accessible.
Exploring Obesity Clinical Trials
Obesity clinical trials are research studies designed to evaluate new treatments, medications, or behavioral strategies for managing and reducing excess weight.
These clinical trials play a vital role in discovering safer and more effective solutions for individuals struggling with obesity, especially when traditional methods have failed.
Participants often gain access to innovative therapies, while contributing to advancements that can benefit others in the future.
FAQS
Does GLP-1 speed up metabolism?
Synthetic GLP-1 medications enhance the body’s natural processes by intensifying hormone activity that regulates appetite and metabolism, leading to greater weight loss and improved metabolic control.
Does GLP-1 affect hormones?
Emerging research indicates that GLP-1 receptor agonists influence hormonal balance, lipid metabolism, and inflammation, potentially providing therapeutic benefits for reproductive health and metabolic changes during menopause.
Who should avoid GLP-1?
GLP-1 receptor agonists may not be suitable for individuals with a history of pancreatitis, kidney disease, or gallbladder issues.
Conclusion
In the discussion of GLP-1 medications vs. traditional weight loss, both approaches offer unique advantages and challenges. GLP-1 medications provide a biology-based solution, often resulting in faster and more significant weight loss, especially for individuals with obesity or metabolic conditions. However, they can be costly and require ongoing use. Traditional methods promote lifestyle changes through diet, exercise, and behavioral strategies but often yield slower, less predictable outcomes. Ultimately, the best approach depends on individual needs, medical history, and long-term goals.