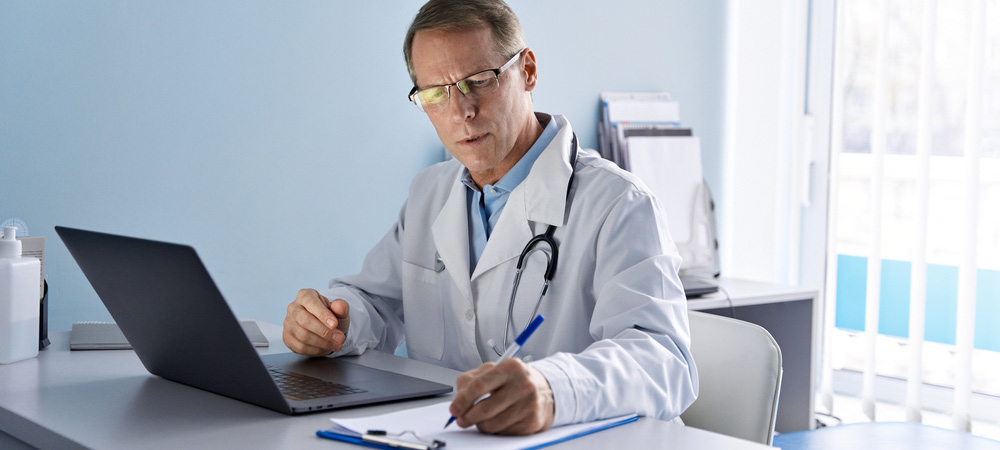
Clinical trials are the backbone of medical advancements, offering a structured and scientifically rigorous means to evaluate the efficacy and safety of new treatments, drugs, and medical devices. These trials have been centralized, requiring participants to visit specific locations for assessments and treatments. A significant shift is taking place in the world of clinical research with the advent of decentralized or distributed clinical trials. This innovative approach is transforming how trials are conducted, making them more accessible, efficient, and patient-centric. In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into what decentralized clinical trials are, their benefits, and a comparison between centralized and distributed clinical trials.
What Is Decentralized Clinical Trials?
Decentralized clinical trials (DCTs) are a modern approach to clinical research that leverages digital technologies and remote methodologies to conduct various trial activities outside traditional clinical settings. Unlike conventional centralized trials, which require participants to travel to a central location, these clinical trials enable many trial-related processes to occur in participants’ homes or local environments. However, this shift is facilitated by advancements in telemedicine, mobile health (mHealth) technologies, and wearable devices, which allow for real-time data collection and remote monitoring.
The concept of distributed clinical trials revolves around the idea of bringing the trial to the participant rather than bringing the participant to the trial. Also, this approach enhances participant convenience and increases the reach and inclusivity of clinical trials, potentially accelerating the pace of medical research and development.
Also Read: Benefits of Clinical Research & The Importance of Clinical Trials
Benefits of Decentralized Clinical Trials
Decentralized clinical trials offer many benefits that address some longstanding challenges associated with traditional centralized trials. Here are some of the key advantages:
1) Improved Patient Accessibility and Engagement
One of the most significant benefits of distributed clinical trials is improved patient accessibility. However, traditional trials often require participants to make frequent visits to a clinical site, which can be a significant burden, especially for those who live in remote areas or have mobility issues. Decentralized trials, on the other hand, allow participants to take part in the trial from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for travel and making it easier for a more diverse population to participate.
Decentralized trials often incorporate digital tools that enhance patient engagement. For instance, mobile apps and wearable devices can provide real-time feedback, reminders, and educational materials, keeping participants informed and motivated throughout the trial.
2) Enhanced Data Collection and Real-Time Monitoring
Distributed clinical trials leverage technology to collect data more efficiently and accurately. However, wearable devices, sensors, and mobile health applications can continuously monitor participants’ vital signs and other health metrics, providing a wealth of real-time data. In addition, this continuous data collection allows researchers to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the treatment’s effects and participants’ health status over time.
Remote monitoring and telehealth consultations enable researchers to promptly address any issues or adverse events, enhancing participant safety and trial integrity.
3) Increased Participant Diversity
Traditional clinical trials often struggle to enroll a diverse participant population due to geographical and logistical barriers. Decentralized clinical trials can overcome these barriers by enabling remote participation, which allows individuals from various regions, ethnicities, and socioeconomic backgrounds to take part in the trial. This increased diversity can lead to more robust and generalizable trial results, ultimately improving the applicability of the findings to a broader population.
4) Reduced Participant Burden and Improved Retention
Frequent travel to clinical sites and time-consuming visits can be significant burdens for trial participants, leading to higher dropout rates. Decentralized trials minimize these burdens by allowing participants to complete many trial activities remotely. However, this convenience can lead to improved participant retention and adherence to the trial protocol, resulting in more reliable and complete data.
5) Faster Trial Initiation and Completion
The logistical complexities of traditional clinical trials can lead to delays in trial initiation and completion. Distributed clinical trials can streamline these processes by reducing the need for physical infrastructure and on-site staff. Digital recruitment methods, electronic informed consent, and remote data collection can expedite trial setup and execution, potentially accelerating the timeline for bringing new treatments to market.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Clinical Trials
To fully understand the advantages and implications of decentralized clinical trials, it’s essential to compare them with traditional centralized trials. While both approaches aim to evaluate the safety and efficacy of medical interventions, they differ significantly in their methodologies and execution.
Study Design and Execution
Centralized Clinical Trials:
In centralized trials, participants are required to visit a central clinical site for all trial-related activities, including screening, treatment administration, and follow-up assessments. This approach relies heavily on the physical presence of participants and clinical staff, making it logistically intensive.
Decentralized Clinical Trials:
Decentralized trials distribute trial activities across various locations, including participants’ homes and local healthcare facilities. Digital technologies enable remote data collection, telehealth consultations, and virtual monitoring, reducing the need for centralized infrastructure.
Participant Recruitment and Enrollment
Centralized Clinical Trials:
Recruitment for centralized trials often involves advertising and outreach efforts to attract participants who live near the clinical site. This can limit the geographic diversity of the participant pool and may require significant travel for some individuals.
Decentralized Clinical Trials:
Decentralized trials leverage digital recruitment strategies, such as online advertisements and social media campaigns, to reach a broader audience. Remote screening and electronic informed consent processes make it easier for participants from diverse locations to enroll in the trial.
Data Collection and Monitoring
Centralized Clinical Trials:
Data collection in centralized trials typically occurs during scheduled site visits, where participants undergo various assessments and provide samples. Monitoring is conducted on-site by clinical staff.
Decentralized Clinical Trials:
Decentralized trials utilize wearable devices, mobile health apps, and remote sensors to collect data continuously and in real time. Telehealth consultations and virtual monitoring allow researchers to stay connected with participants and promptly address any issues.
Participant Experience
Centralized Clinical Trials:
Participants in centralized trials may face challenges such as travel expenses, time away from work or family, and the inconvenience of frequent site visits. These factors can contribute to higher dropout rates.
Decentralized Clinical Trials:
Decentralized trials offer a more convenient and flexible experience for participants, as they can complete many trial activities from home. Reduced travel and time commitments can enhance participant satisfaction and retention.
Cost and Resource Allocation
Centralized Clinical Trials:
Centralized trials require significant investment in physical infrastructure, on-site staff, and travel expenses for participants. These costs can be substantial, especially for large-scale trials.
Decentralized Clinical Trials:
Decentralized trials can reduce costs by minimizing the need for physical infrastructure and on-site staff. Remote data collection and digital tools can streamline trial processes and allocate resources more efficiently.
Regulatory Considerations
Both centralized and decentralized clinical trials must adhere to regulatory guidelines to ensure participant safety and data integrity. Decentralized trials may face unique regulatory challenges, such as ensuring the security and privacy of remote data collection and addressing the variability in local healthcare practices. Regulatory agencies are increasingly recognizing the potential of decentralized trials and are developing guidelines to support their implementation.
Conclusion
Decentralized clinical trials represent a paradigm shift in clinical research, offering a more patient-centric, efficient, and inclusive approach to evaluating medical interventions. By leveraging digital technologies and remote methodologies, decentralized trials can overcome many of the challenges associated with traditional centralized trials, such as limited participant accessibility, high dropout rates, and logistical complexities. The benefits of distributed clinical trials include improved patient engagement, enhanced data collection, increased participant diversity, and faster trial initiation and completion.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, distributed clinical trials are poised to play a pivotal role in advancing medical research and bringing new treatments to market more quickly and efficiently. Researchers, sponsors, and regulatory agencies must work collaboratively to address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by this innovative approach, ensuring that decentralized trials can deliver on their promise of transforming the future of clinical research.